The Complete Magnesium Guide: Symptoms, Benefits & Best Types to Take
Magnesium is one of the most important minerals in the human body — yet also one of the most commonly overlooked. It plays a role in over 600 biochemical reactions, including energy production, muscle relaxation, nerve function, sleep regulation, blood sugar control, hormone balance, and heart rhythm.
Despite its importance, studies estimate that 50–70% of people do not meet their daily magnesium needs.
Watch the video below to understand how different forms compare and how to pick the right option for your needs.
Table Of Contents
- KEY TAKEAWAYS
- What Does Magnesium Do in the Body?
- Why Magnesium Deficiency Causes So Many Symptoms
- Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
- The Benefits of Magnesium
- The Best Types of Magnesium (And Which One YOU Should Take)
- What Forms of Magnesium to Avoid
- Should You Take a Single Magnesium or a Combination?
- How Much Magnesium Should You Take?
- Do You Need a Magnesium Test?
- Best real-world approach
- Lifestyle Tips to Improve Magnesium Levels Naturally
- Final Thoughts
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The early and hidden signs of magnesium deficiency
- How magnesium impacts your brain, mood, sleep, heart, hormones, gut and nerves
- What the different types of magnesium actually do
- Which magnesium is best for your symptoms
- How much to take, when to take it, and what to avoid
- The most reliable way to test magnesium levels (and when testing isn’t necessary)
Let’s dive into everything you need to know about magnesium and how to use it to support your health.
What Does Magnesium Do in the Body?
Magnesium is involved in hundreds of biochemical reactions, and even mild deficiency can impact multiple systems at once. Here’s a deeper look at the core functions of magnesium and why it’s so essential for optimal health.
1. Energy Production (ATP)
Magnesium is required to activate ATP — the molecule your cells use for energy. In fact, ATP must be bound to magnesium to be biologically active.
Without enough magnesium, your cells simply can’t generate or use energy efficiently, leading to fatigue, brain fog, poor exercise tolerance, and slow recovery.
2. Muscle Relaxation

Muscles contract when calcium enters the cell and relax when magnesium helps push calcium back out.
When magnesium is low, muscles stay partially contracted, which can lead to tightness, cramps, spasms, tension headaches, and restless legs. This is why nighttime magnesium often reduces muscle tension and improves sleep quality.
3. Nervous System Calm (GABA & NMDA Balance)

Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters by supporting calming GABA activity and reducing overstimulation at NMDA receptors.
Low magnesium can make your nervous system more reactive, contributing to anxiety, irritability, sensitivity to noise, and difficulty winding down. When levels are adequate, the brain is more stable, resilient, and balanced.
4. Sleep Regulation

Magnesium supports the natural transition into sleep by relaxing the nervous system and muscles, reducing nighttime cortisol, and helping regulate circadian rhythms.
It doesn’t work like a sedative — instead, it removes the physiological “tension” that interferes with falling asleep and staying asleep.
Many people find their sleep becomes deeper and more restorative once magnesium levels improve.
You might also be interested in 12 Tips To Sleep Better Tonight, check it out!
5. Blood Sugar Control
Magnesium is essential for insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Low magnesium can contribute to blood sugar swings, increased cravings, mid-afternoon crashes, and difficulty maintaining stable energy throughout the day.
Studies show that people with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes often have significantly lower magnesium levels, and improving magnesium status helps stabilize glucose control.
6. Hormone Balance

Magnesium plays a key role in hormone regulation, including estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, and thyroid hormone.
It helps the liver metabolize estrogen efficiently and supports progesterone production, which is why magnesium often improves PMS symptoms and reduces menstrual cramps.
Magnesium also helps buffer the stress response by regulating the HPA axis.
7. Heart Rhythm & Blood Pressure

Magnesium supports normal electrical conduction in the heart, which helps maintain a steady rhythm and reduces palpitations in people who are deficient.
It also relaxes vascular smooth muscle, which can support healthy blood pressure levels.
Many people describe magnesium as helping their heart feel “quieter” and less reactive to stress.
8. Vitamin D Activation

Vitamin D requires magnesium at every step of its activation — from synthesis in the skin to conversion in the liver and kidneys.
If magnesium is low, vitamin D supplements may not raise blood levels as expected.
This is why people who feel “no benefit” from vitamin D often improve once magnesium is corrected.
Why Magnesium Deficiency Causes So Many Symptoms
Because magnesium participates in such a vast range of metabolic processes — energy, nerves, muscle function, digestion, hormones, sleep, immunity — deficiency rarely shows up as just one symptom.
Instead, people often experience a cluster of issues that seem unrelated.
Once magnesium levels improve, multiple systems often improve at the same time, making it one of the most impactful nutrients to optimize.
Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency symptoms are common and often brushed off as “stress,” “anxiety,” or “getting older.”
Below are the most reliable signs your body may need more magnesium, grouped into clear categories.
1. Neuromuscular Symptoms

These are often the earliest signs:
- Eye twitching
- Muscle cramps (especially at night)
- Foot or calf spasms
- Muscle tightness
- Tingling or pins-and-needles
- Restless legs
- Tension headaches
These symptoms occur because nerves fire too easily when magnesium is low.
2. Sleep and Energy Symptoms

Magnesium is essential for calming the nervous system and producing energy.
Signs include:
- Fatigue (even after sleeping)
- Feeling “wired but tired”
- Trouble falling asleep
- Waking up frequently at night
- Low daytime energy
- Afternoon crashes
If you wake up tired despite 7–9 hours of sleep, magnesium may play a role.
3. Mood and Cognitive Symptoms

Low magnesium affects brain chemistry and neurotransmitter balance.
Common symptoms:
- Anxiety
- Feeling easily overwhelmed
- Irritability
- Noise sensitivity
- Brain fog
- Poor concentration
- Low mood or emotional slumps
Magnesium helps regulate serotonin and reduces overstimulation in the brain.
4. Heart and Cardiovascular Symptoms

Because magnesium stabilizes electrical conduction, deficiency can show up as:
- Heart palpitations
- Skipped beats
- Mild blood pressure elevation
- Chest tightness (muscle-related)
Magnesium is often used in hospital settings for arrhythmias and high blood pressure in pregnancy — highlighting its importance.
5. Digestive and Metabolic Symptoms

Magnesium supports digestion, blood sugar, and hormone balance.
Common signs:
- Constipation
- PMS symptoms
- Menstrual cramps
- Sugar cravings
- Blood sugar swings
- Fluid retention
- Slow digestion
6. Stress Sensitivity

If stress hits you harder than it used to — or you can’t “come down” after stress — this can be a magnesium issue.
Chronic stress also depletes magnesium further, creating a vicious cycle.
The Benefits of Magnesium
Correcting magnesium deficiency can improve multiple systems at once. Here are the most clinically relevant benefits.
1. Better Sleep
Magnesium supports GABA activity and reduces nighttime cortisol.
Many people experience deeper, more restorative sleep with magnesium glycinate.
2. More Calm, Less Anxiety
Because magnesium modulates neurotransmitters, it helps your nervous system shift from “fight-or-flight” into a calm parasympathetic state.
3. Improved Energy & Less Fatigue
By supporting ATP production, magnesium helps stabilise energy levels throughout the day.
Malate is especially good for energy and mitochondrial support.
4. Reduced Muscle Tension & Cramping
Great for athletes, people with restless legs, and anyone who sits for long periods.
5. Heart Rhythm & Blood Pressure Support
Magnesium helps the heart maintain a steady rhythm and relaxes blood vessel walls, supporting healthy blood pressure.
6. Better Blood Sugar Control
Magnesium improves insulin sensitivity — a key issue for many people with fatigue or metabolic health challenges.
7. Hormonal Balance & PMS Relief
Many women experience fewer PMS symptoms, less cramping, and better sleep when they correct magnesium levels.
8. Vitamin D Activation
If you take vitamin D but levels remain low, magnesium may be the missing piece.
The Best Types of Magnesium (And Which One YOU Should Take)
Not all magnesium supplements work the same. The “form” determines:
- Absorption
- Targeted benefits
- Side effects
- How it affects your nervous system
Here are the most useful forms.
1. Magnesium Glycinate
|
Best for |
Sleep, anxiety, stress, muscle tension |
|
Why |
Glycine promotes relaxation & supports GABA |
|
Digestive Tolerance |
Gentle on digestion |
|
Ideal time |
Evening |
|
Highlight |
This is the most calming, well-tolerated form. |
2. Magnesium Malate
|
Best for |
Energy, muscle fatigue, fibromyalgia, daytime tiredness |
|
Why |
Supports ATP production |
|
Digestive Tolerance |
Stimulating, not sedating |
|
Ideal time |
Morning |
|
Highlight |
Excellent for mitochondrial support. |
3. Magnesium Taurate
|
Best for |
Heart palpitations, stress, blood pressure, metabolic health |
|
Why |
Taurine calms nerves & stabilises heart rhythm |
|
Digestive Tolerance |
XX |
|
Ideal time |
Anytime |
|
Highlight |
Great for people with stress + cardiovascular symptoms. |
4. Magnesium Threonate (L-Threonate)
|
Best for |
Brain fog, focus, memory, mental clarity |
|
Why |
Crosses blood-brain barrier |
|
Ideal time |
Morning or evening |
|
Highlight |
The “brain magnesium.” |
5. Magnesium Citrate
|
Best for |
Constipation, general magnesium boosting (daytime) |
|
Why |
Highly absorbable but can loosen stools |
|
Ideal time |
Morning / daytime |
|
Highlight |
Great for people who want good absorption but not sedation. |
What Forms of Magnesium to Avoid
❌ Magnesium Oxide
Poor absorption (~4%).
Mainly acts as a laxative.
❌ Magnesium Carbonate / Hydroxide
Antacids — not useful for raising magnesium levels.
❌ Magnesium Aspartate / Glutamate
Excitatory compounds can overstimulate the nervous system.
Not ideal for anxiety, fatigue, or sleep issues.
Should You Take a Single Magnesium or a Combination?
Use a single magnesium form if you have one clear symptom

Examples:
- Sleep → Glycinate
- Energy → Malate
- Brain fog → Threonate
- Palpitations → Taurate
- Constipation → Citrate
Use combination magnesium if your symptoms overlap

Examples:
- Stress + sleep + cramps → Glycinate + Taurate
- Brain fog + fatigue → Threonate + Malate
- Low energy + constipation → Malate + Citrate
Watch Out for Proprietary Blends
Many magnesium products use proprietary blends, which list several forms of magnesium but don’t disclose how much of each one is included.
This allows companies to include a tiny amount of the beneficial forms (like glycinate or malate) while using cheaper fillers like magnesium oxide to bulk up the total.
Without exact amounts listed, there’s no way to know what you’re actually getting — making it impossible to dose properly or know if the product will be effective.
Always choose supplements that clearly show the amount of each magnesium type on the label.
How Much Magnesium Should You Take?
General guideline:
300–400 mg of elemental magnesium per day
Start lower if sensitive.
Timing:
- Glycinate → evening
- Malate → morning
- Taurate → anytime
- Threonate → flexible
- Citrate → morning or daytime
Who should be careful?
- People with kidney disease
- Severe low blood pressure
- People on certain medications (check with a doctor)
Do You Need a Magnesium Test?
The truth is:
Standard blood tests for magnesium are not accurate.
- Serum magnesium → reflects only the 1% in blood
- RBC magnesium → better, reflects intracellular levels – good but not essential to do before supplementing
- Magnesium loading tests → most accurate, rarely used clinically
Best real-world approach
Try magnesium for 2–3 weeks and monitor improvements in:
- Sleep
- Stress
- Cramps
- Energy
- Digestion
- Mood
Magnesium is very safe for most people — and deficiency is common
Lifestyle Tips to Improve Magnesium Levels Naturally
Alongside supplementation:
Eat magnesium-rich foods
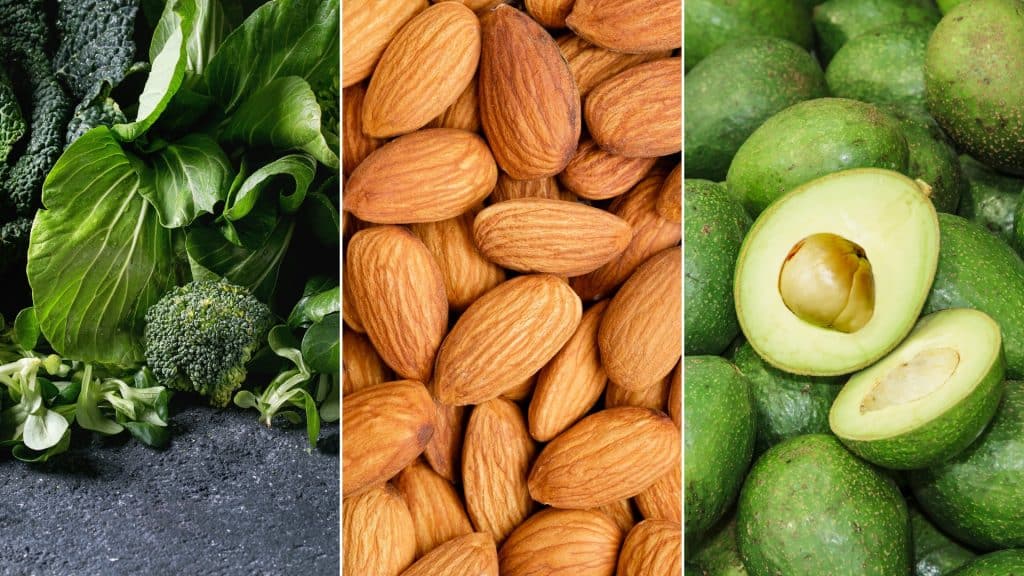

- Leafy greens
- Pumpkin seeds
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Avocado
- Dark chocolate
- Legumes
- Whole grains
Reduce magnesium depletion by limiting

- Excess sugar
- Excess caffeine
- Chronic stress
- Alcohol
- PPIs / acid blockers
- Highly processed foods
Final Thoughts
Magnesium deficiency is incredibly common — and often missed.
Because magnesium impacts so many systems (sleep, stress, energy, hormones, heart, digestion, mood), getting the right amount can have profound effects on your health.
The key is choosing the right magnesium type for your symptoms and taking it consistently for 2–3 weeks to assess how you feel.
If you want to check your magnesium levels along with all your vitamins and minerals I recommend the Vibrant Wellness Micronutrient panel.











